Overview
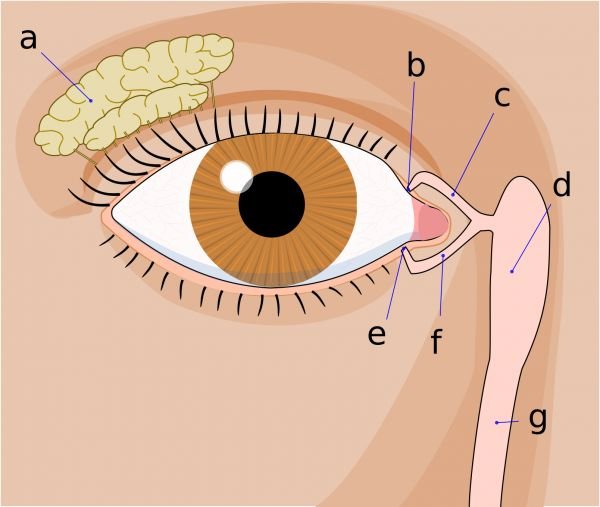
Dacryocystitis is an infection or inflammation of the tear sac (lacrimal sac), which is located near the inner corner of the eye. It usually occurs when the tear duct becomes blocked, allowing bacteria to grow and cause infection. Symptoms of dacryocystitis include pain, redness, swelling near the eye, excessive tearing, and sometimes discharge or pus. It can affect people of all ages, but is more common in infants and older adults. Treatment typically involves antibiotics, and in some cases, a minor surgical procedure may be needed to clear the blockage and restore normal tear drainage.
How Its Works?
Dacryocystitis happens when the tear drainage system in the eye becomes blocked, usually in the tear duct. Tears normally flow from the eye into the nose through a small duct. When this duct is blocked, tears can’t drain properly and start to build up. This creates a moist environment where bacteria can grow, leading to an infection in the tear sac. As a result, the area near the inner corner of the eye becomes red, swollen, painful, and may even produce pus or discharge.
 Treating dacryocystitis early helps relieve pain, reduce swelling, and prevent the infection from spreading to other parts of the face or eyes. Proper treatment, which may include antibiotics or minor surgery, restores normal tear drainage and helps protect your vision. Early care also lowers the risk of future infections and helps maintain overall eye health and comfort.
Treating dacryocystitis early helps relieve pain, reduce swelling, and prevent the infection from spreading to other parts of the face or eyes. Proper treatment, which may include antibiotics or minor surgery, restores normal tear drainage and helps protect your vision. Early care also lowers the risk of future infections and helps maintain overall eye health and comfort.