Overview
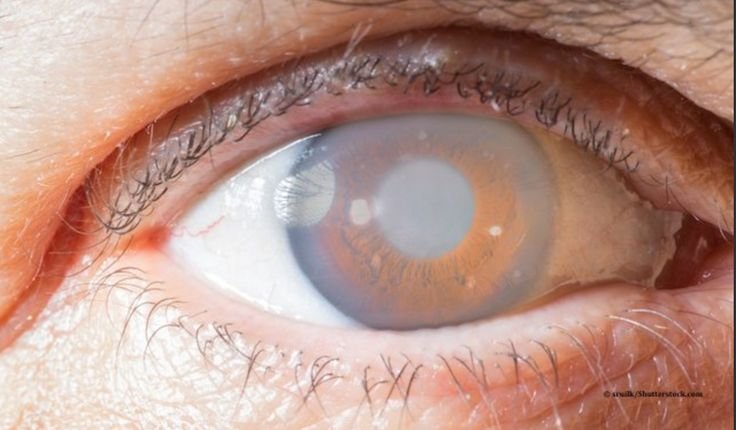
Glaucoma is an eye condition that damages the optic nerve, which is essential for good vision. It usually happens when there is a build-up of pressure inside the eye. If not treated early, glaucoma can lead to permanent vision loss or even blindness. Often called the "silent thief of sight," it usually has no early symptoms, which makes regular eye checkups very important. Treatment options include eye drops, medications, laser procedures, or surgery to lower the eye pressure and protect vision.
How Its Works?
Glaucoma works by increasing the pressure inside the eye, known as intraocular pressure (IOP). This pressure builds up when the fluid inside the eye doesn’t drain properly. Over time, the high pressure can damage the optic nerve, which carries visual information from the eye to the brain. As the nerve becomes damaged, blind spots start to develop in the field of vision. If left untreated, this damage can lead to permanent vision loss. Regular eye exams can help detect glaucoma early, before serious damage occurs.
 Glaucoma works by slowly damaging the optic nerve due to increased pressure inside the eye. This pressure builds up when the fluid that normally drains from the eye doesn't flow properly. As the pressure rises, it begins to harm the optic nerve, which is responsible for sending visual signals to the brain. Over time, this damage can lead to blurry vision, blind spots, and even permanent blindness if not treated early.
Glaucoma works by slowly damaging the optic nerve due to increased pressure inside the eye. This pressure builds up when the fluid that normally drains from the eye doesn't flow properly. As the pressure rises, it begins to harm the optic nerve, which is responsible for sending visual signals to the brain. Over time, this damage can lead to blurry vision, blind spots, and even permanent blindness if not treated early.